The Importance of Paradontologiya in Modern Dentistry
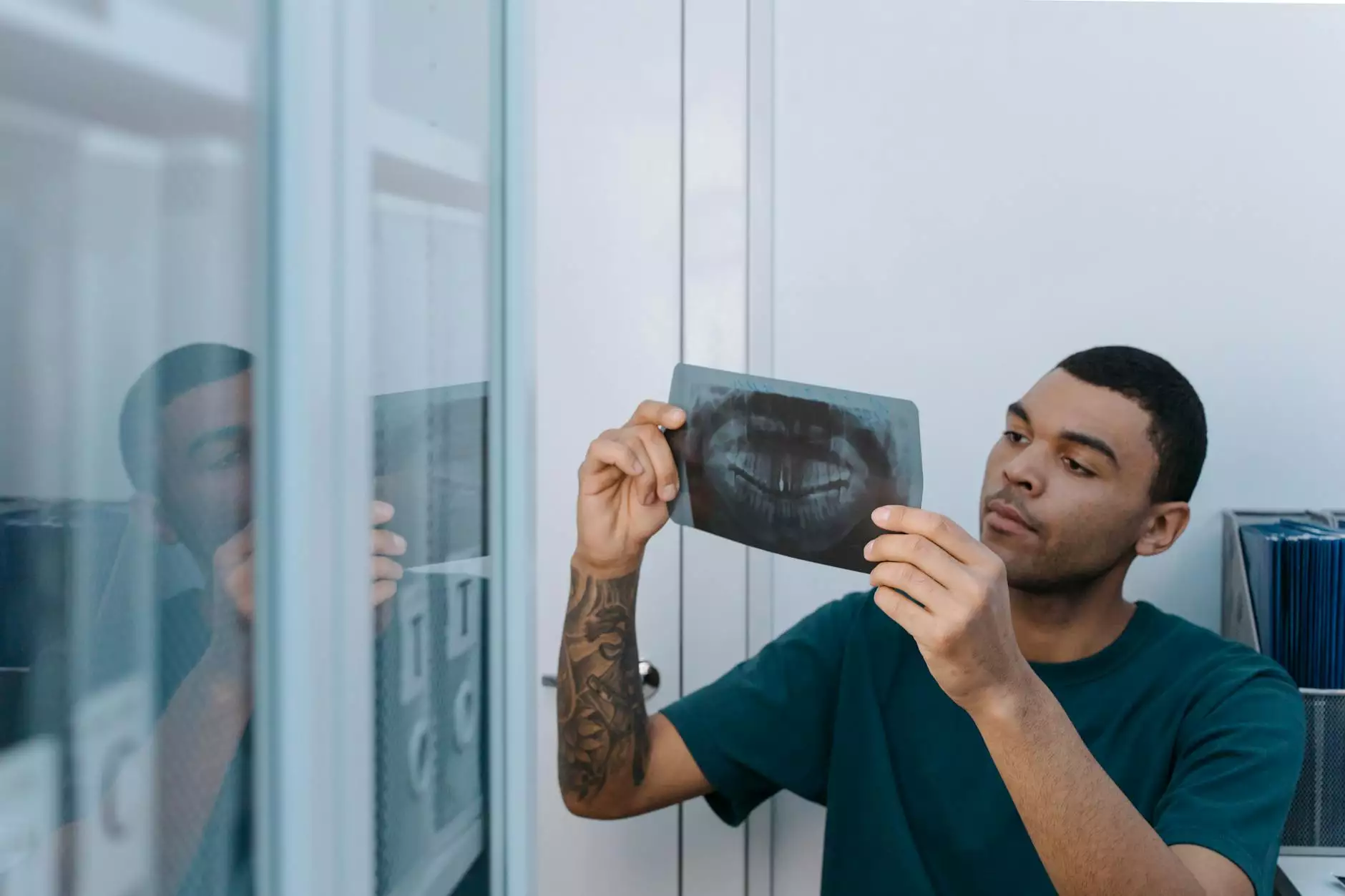

Paradontologiya, or periodontology, is a crucial branch of dentistry that focuses on the supporting structures of the teeth, including the gums, bone, and periodontal ligaments. While many people prioritize the aesthetics of their smiles, the health of these underlying structures is essential for overall oral health. In this article, we will delve deeply into the world of paradontologiya, exploring its importance, common diseases, treatments, and how it relates to general health. We will also discuss how you can maintain healthy gums and support structures through effective dental practices.
Understanding Paradontologiya
The term paradontologiya is derived from the Greek words "para" meaning "around" and "odous" meaning "tooth." Thus, it literally refers to the study of the structures around the teeth. In dentistry, this field examines the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of diseases that affect these supporting tissues.
The Importance of Gums in Oral Health
Healthy gums are essential for several reasons:
- Support for Teeth: Gums provide the necessary protection and support for teeth. They form a seal around the teeth and prevent the entry of pathogenic bacteria.
- Protective Barrier: Gums act as a barrier, protecting the underlying bone and connective tissues from infections that can cause tooth loss.
- Influence on Overall Health: Research shows that periodontal health is linked to systemic health conditions. Poor gum health can contribute to cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and other health issues.
Common Periodontal Diseases
Periodontal diseases can range from mild inflammation to severe damage to the supporting structures of teeth. The most common conditions include:
1. Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease characterized by inflammation, redness, and swelling of the gums. It is often caused by the accumulation of plaque on the teeth. Symptoms include:
- Puffy, swollen gums
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to a more severe form of periodontal disease.
2. Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a more severe gum disease that occurs when gingivitis is left untreated. It involves the destruction of the supporting bone and tissues, leading to tooth mobility and potential loss. Symptoms may include:
- Receding gums
- Formation of pockets between the teeth and gums
- Loose teeth
- Chronic bad breath
Early intervention is crucial to prevent the progression of paradontologiya conditions.
3. Aggressive Periodontitis
This is a rare form of gum disease that occurs in patients who are otherwise healthy. It can lead to rapid loss of gum tissue and supporting bone. Symptoms of aggressive periodontitis include:
- Severe gum inflammation
- Rapid attachment loss and bone destruction
- Family history of periodontal disease
Risk Factors for Periodontal Disease
Several factors can increase the risk of developing periodontal disease, including:
- Smoking: Tobacco use significantly contributes to the progression of gum disease.
- Diabetes: Diabetes can impair blood flow and reduce the body’s ability to fight infections, including gum infections.
- Hormonal Changes: Changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can make gums more sensitive and susceptible to disease.
- Medications: Certain medications can affect oral health by reducing saliva flow, which protects gums.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A diet lacking essential nutrients can negatively impact gum health.
Diagnosis of Periodontal Diseases
Diagnosing periodontal disease typically involves a thorough dental examination and a medical history review. Dentists will:
- Examine the gums for signs of inflammation, bleeding, or recession.
- Measure pocket depths around the teeth with a probe.
- Take X-rays to assess the bone level and any loss.
Early detection is key to effective treatment and management of paradontologiya.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Diseases
Depending on the severity of the disease, treatment options may vary:
1. Non-Surgical Treatments
For early-stage gum disease, non-surgical treatments can be very effective, including:
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure removes plaque and tartar from the surfaces of the teeth and below the gum line.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to help control bacterial infection.
- Modified Oral Hygiene Instructions: Dentists may provide instructions for improved at-home care.
2. Surgical Treatments
If periodontal disease is more severe, dental professionals may recommend surgical solutions, including:
- Flap Surgery: This procedure involves lifting back the gums to remove tartar deposits and then securing the gums back in place.
- Bone Grafting: This technique is designed to replace lost bone tissue and stabilize the tooth.
- Tissue Grafting: This involves taking tissue from another site to help restore lost gum tissue.
Preventive Measures for Oral Health
Preventing periodontal disease is possible with proper oral hygiene practices. Here are some effective measures:
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visiting your dentist at least twice a year will allow for professional cleanings and early detection of any issues.
- Daily Oral Hygiene: Brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports good gum health.
- Avoid Tobacco: Quitting smoking can significantly reduce your risk of developing gum diseases.
Conclusion
Understanding paradontologiya is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing serious dental issues. By recognizing the importance of gum health, being aware of periodontal diseases, and following preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk for these conditions. Consulting with qualified professionals, such as those at ustomatologa.kiev.ua, is vital for personalized advice and treatment. Prioritize your gum health and take proactive steps to ensure a healthy, beautiful smile for years to come.